The Cosmos blockchain was developed to facilitate communication between distributed ledgers without relying on a centralized server. The Cosmos white paper was published in 2016, and the network was soon regarded as the Internet of blockchains by its founders who wanted to create an interoperable platform of open-source blockchains that could streamline transactions between them.
Since the inception of blockchain, interoperability has been a challenging task for developers.
Interoperability is what enables communication between two or more systems. Think of emails from a Gmail account communicating with a Hotmail one. Or, an Android phone that is allowed to share data with Apple's iOS.
Single structures are created first, like in the case of a specified blockchain. Still, it's necessary to get the systems to communicate. Otherwise, they're not of much use and may represent a barrier to technology adoption.
Cosmos is the first entirely free platform to enable interoperability between different systems including Binance Chain, Terra and Crypto.org, to name a few, with over $151 billion of digital assets under management.
Cosmos (ATOM) is the cryptocurrency that powers and secures the ecosystem of blockchains designed to scale and interoperate between one another.
How does Cosmos work?
The Cosmos network is an ever-expanding ecosystem of apps and services interconnected.
It uses hubs, the Tendermint consensus algorithm, and the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol to ensure that blockchains can communicate securely.
Some platforms communicate with each other using smart contracts. Through this process, tokens are locked in on one platform and then the asset's corresponding amount is minted on the other. The wrapped tokens are a typical example of this process.
Rather than sending Bitcoin (BTC) from the Bitcoin blockchain to another platform like Ethereum, the BTC gets locked in a functional blockchain that provides the service. The correspondent amount such as wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC) is issued in pegged tokens on another blockchain.
In contrast, Cosmos offers open-source tools to allow developers to build decentralized and sovereign blockchain applications called zones instead of relying on one single chain. The zones are Cosmos smart contracts.
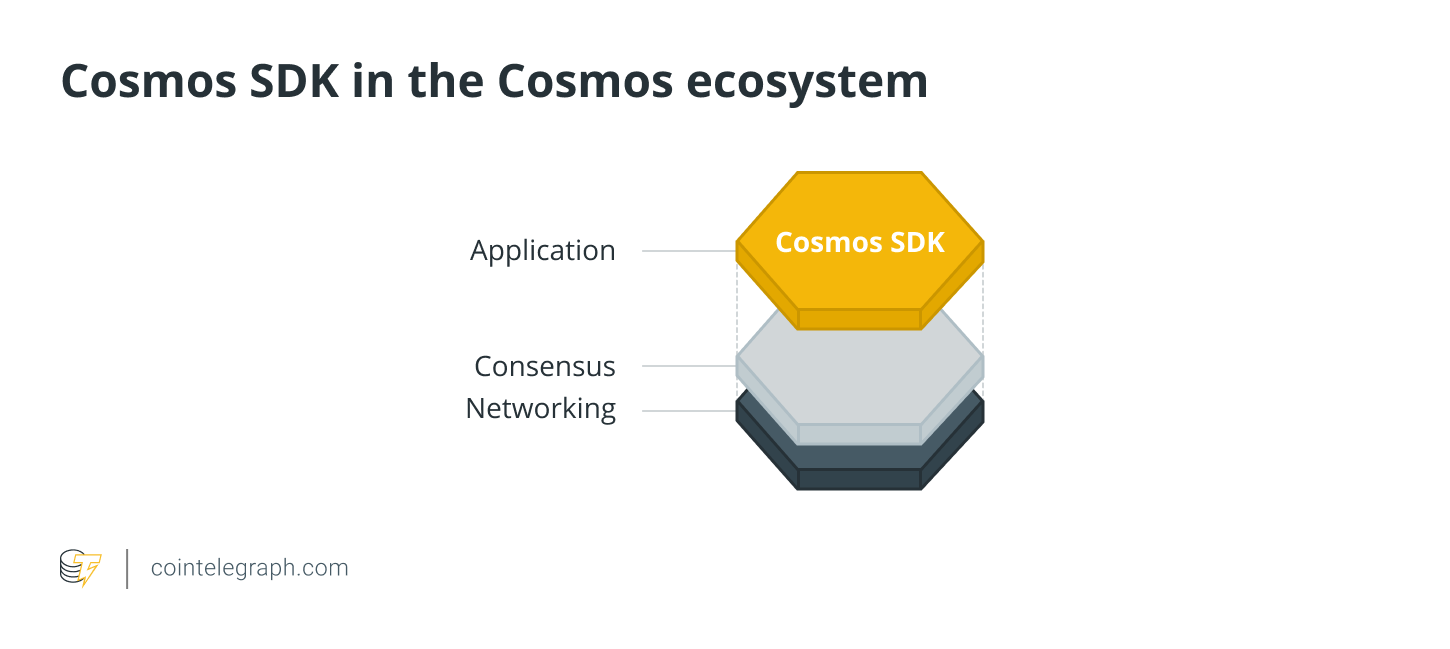
The Cosmos team has built the software development kit (SDK) that allows developers to build zones faster, simpler and cheaper than other platforms like Ethereum.
It minimizes complexity by offering the most common functionality among blockchains such as staking, governance and tokens through well-known and simple-to-use software development programs like GO. Developers have the maximum freedom and flexibility to create plugins and add any features they want.
Cosmos hubs
Each zone connects to another zone through hubs. Cosmos Hub is the main one, but other hubs are also available.
Any zone or hub does not necessarily have to work with another, but each new zone is linked to the Cosmos Hub, the first blockchain launched on the Cosmos network that keeps a record of each zone's state and vice versa.
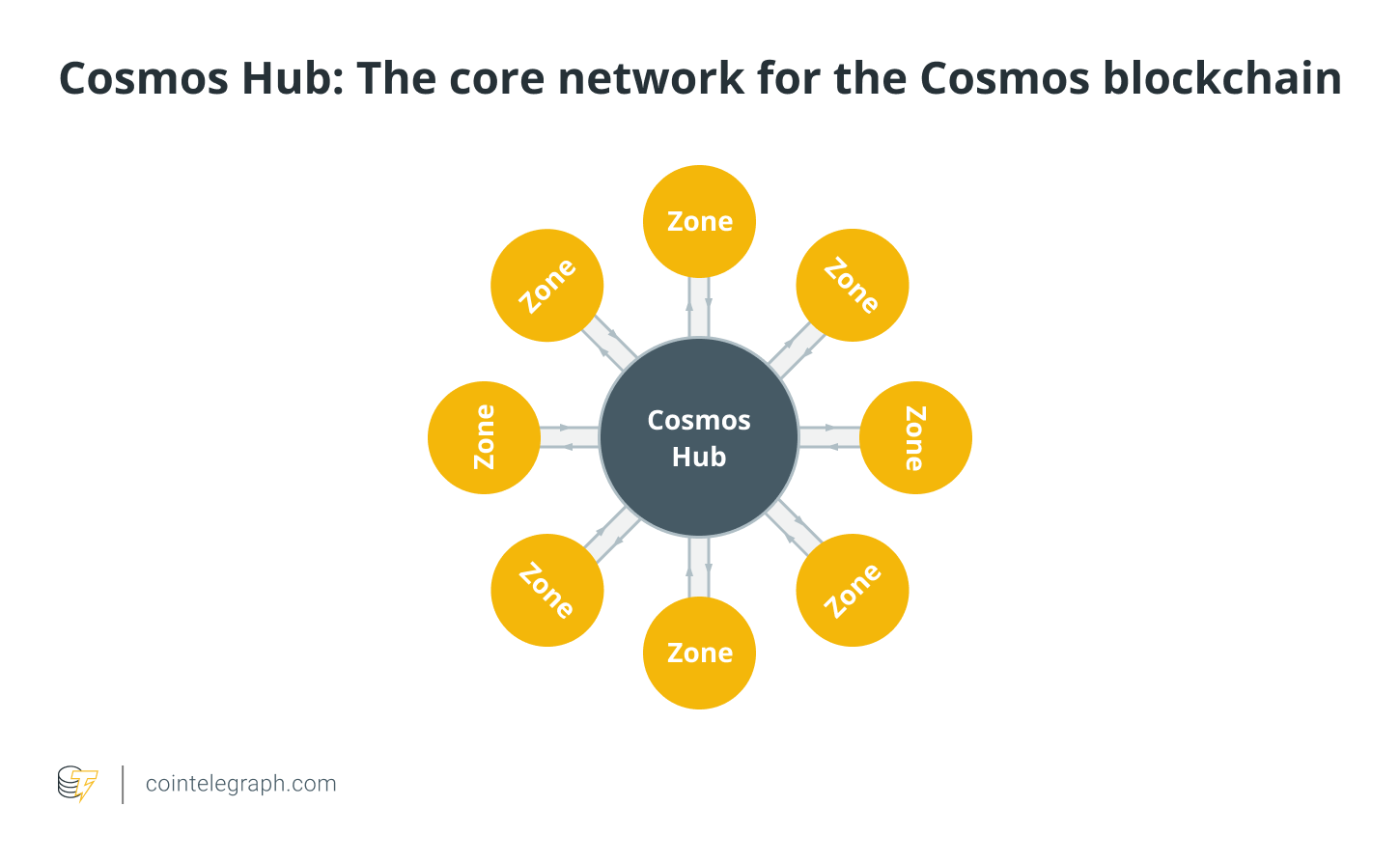
Each zone can function autonomously, from authenticating accounts and transactions to creating and distributing new tokens and executing blockchain changes.
Beyond facilitating interoperability between all the zones within the network by keeping track of their states, Cosmos hub also allows interoperability with proof-of-work (PoW) blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum through bridges, even if they don't meet the requirements of the Cosmos protocol. An upcoming bridge to Polkadot is also awaited with eagerness by crypto experts and enthusiasts.
Tendermint Byzantine fault tolerance (BFT)
Cosmos SDK tools use by default the Tendermint Byzantine fault tolerance (BFT) engine consensus protocol to secure the network, yet others can also be used. Tendermint BFT allows developers to build blockchains without coding them from scratch.
The Tendermint BFT algorithm validates transactions and executes blocks to the blockchain. It uses a protocol called the application blockchain interface to connect to applications.
The protocol functions through a proof-of-stake (PoS) governance mechanism that supports integrating the computers' distributed network running Cosmos Hub.
Participants in the network can stake ATOM and earn rewards. The top 100 stakers can become validator nodes to power the blockchain and vote on changes. The higher the amount of ATOM staked, the higher the voting power for the validators.
Users can also choose to delegate their tokens to validators and interchange them. This incentivizes validators to perform honestly. Users can easily switch between the validators they delegate ATOM to, depending on their voting preferences.
Hubs and zones communicate through the Inter-Blockchain Communication, or IBC, protocol, which allows them to interact.
Inter-Blockchain Communication protocol
IBC is a protocol that allows the transmission of secure messages between heterogeneous blockchains/zones and connects them to the Cosmos hub. This innovative process enables users to freely and securely exchange assets and data across sovereign (autonomous) and decentralized blockchains.
The Cosmos Hub is regarded as a service provider to the chains that must connect to it to become interoperable. Any sovereign blockchain with different applications, validators, and consensus mechanisms can still communicate with each other and exchange data, regardless of their functions and business objectives.
Cosmos blockchains can practically do anything they want using IBC from crypto to nonfungible token (NFT) transfers, as well as cross-chain smart contracts. Any cross-chain application can be built thanks to the IBC.
What problem does Cosmos solve?
Cosmos' objective is to enable communication between all blockchains while solving the three main blockchain problems: sovereignty, scalability and sustainability.
Sovereignty
The Cosmos free SDK allows developers to build sovereign blockchain apps without ongoing costs. These blockchains can easily interconnect without relying on smart contracts to exist on a different blockchain, thereby avoiding high transaction fees due to network congestion while developing better scaling features.
This will boost innovative functionalities in decentralized finance (DeFi), NFTs, gaming, decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), social networks, marketplaces and the economy that relies on the internet, especially the ownership economy in which everyone has a stake.
Scalability
Cosmos interoperability is what guarantees the functioning of a scalable system. By integrating to Cosmos interoperability model of shared communication standards, any type of sovereign blockchain will be able to communicate with each other and contribute to the evolution of its protocol design.
Cosmos scalability can be obtained by duplicating a blockchain to relieve congestion or splitting the apps into multiple application-specific blockchains. Interchain token transfers allow these multiple chains to continue one network.
Sustainability
Sustainability is assured by the PoS consensus algorithm, which secures the network. PoS reduces carbon footprint by 99% compared with the PoW consensus algorithm.
Cosmos vs. Ethereum
Even though Ethereum developers have supported an upcoming switch to PoS for years, the platform is still sitting on a PoW consensus algorithm, making it less sustainable than Cosmos.
Scalability is another major issue for Ethereum. Sometimes, it may take minutes to even hours to execute an Ethereum transaction.
Instead, Cosmos Tendermint BFT proof-of-stake algorithms can handle up to thousands of transactions per second, making the whole process much faster and cheaper than Ethereum's gas fees that might be extremely high at times, depending on the blockchain traffic.
In Ethereum, complex financial instruments are dealt with permissionless smart contracts with specific functions to build the whole ecosystem. In Cosmos, each smart contract or application is essentially a blockchain itself, meaning that they won't interfere with each other while reassuring the smooth transaction process.
Cosmos offers a developer-friendly design to build sovereign blockchains quickly and cheaply. Its interoperable system allows simple communication between blockchains which Ethereum does not allow unless the rather complicated and unsecure exchange of wrapped tokens is used.
On the other hand, the primary benefit of using Ethereum is its popularity as a blockchain. Its network effect still makes it the favorite platform for DeFi, NFTs and the Metaverse, representing blockchain's most trendy features at present and will likely be in the future.
Cosmos vs. Polkadot
Although Cosmos and Polkadot seem to share the same type of governance, two main differences vastly distinguish them: governance in transactions validation and the transfer of tokens or assets between the systems.
Cosmos hub protocol defines that transactions are validated by the top 100 validators who stake the highest amount of ATOM.
Delegators can choose and change validators' pools to stake tokens and earn rewards at any time. Zones can have their preferred type of governance, ranging from issuing their cryptocurrency rather than ATOM to having their own hub with a different validation system.
Private permissioned blockchain zones can be created alongside public ones, and can easily transfer assets between them.
In Polkadot, parachains are similar to Cosmos' blockchain zones. However, they share the same set of validators, ensuring a unified and strengthened security across the network through the Relay chain, the central coordinating blockchain. Cosmos blockchains connected to the hub do not rely on the same unified security.
While token transfers from one parachain to another are executed via smart contracts on Polkadot, Cosmos' IBC provides easy asset transfers and interaction between chains via IBC and the Cosmos Hub. Cosmos smart contracts are essentially blockchains.
This allows Cosmos to record each transaction in three different places: the two interacting zones and the hub.
Who is behind Cosmos crypto?
The development of Cosmos is the result of cooperation between different teams. Primary resources and funds for its development were allocated by the Swiss Interchain Foundation (ICF), a non-profit organization that funds and supports open-source blockchain projects, and the Tendermint team.
Software developers Jae Kwon and Ethan Buchman co-founded the Cosmos network in 2014 while also creating Tendermint, the consensus algorithm that would power Cosmos. Kwon and Buchman authored the Cosmos white paper in 2016 and later released its software in 2019.
The Interchain Foundation held the first series of fundraising with a two-week initial coin offering (ICO) of the ATOM token in 2017, accumulating over $17 million.
Tendermint Inc. raised $9 million to continue the development of the project through a Series A funding round in 2019. Jae Kwon left the project in early 2020, pledging he would stay involved anyway, while the other co-founder, Ethan Buchman, is still president of the Interchain Foundation Council.
Cosmos has attracted investment from several prominent names in crypto including Paradigm, Bain Capital and 1confirmation.
Is Cosmos a good investment?
Since its inception, ATOM has seen significant gains accounting for an increase of nearly 600% in value. ATOM achieved its all-time high of $38.78 in September 2021.
Although each zone can issue and use its cryptocurrency, ATOM remains the primary token utilized in the Cosmos ecosystem. It plays a crucial role in maintaining interoperability across the network and can be held, spent, sent or staked.
With an increasing number of zones built in the network relying on its security and transparency as a multiasset distributed ledger, ATOM becomes more valuable, especially as adoption boosts. It's convenient for Cosmos users to own and stake ATOM to get the ability to vote on network upgrades other than gaining rewards by doing so.
Investors should be aware that there is no cap on ATOM's circulation supply. Instead, Cosmos adjusts the number of tokens created based on the number of ATOM being staked.
It is easy to invest in Cosmos (ATOM). The cryptocurrency first hit the exchanges in 2019. If you're wondering how to buy the cosmos crypto, all the significant platforms allow trades in the token. Coinbase, Binance, Kraken are only a few of the long list of exchanges that offer the service.
Cosmos staking
Staking ATOM is a necessary step to contribute to the economic security and the governance of the Cosmos ecosystem. It only takes the selection of one or more Cosmos validators to get started with earning rewards in the form of crypto assets. It also grants the right to vote on upgrades and proposals that will determine the future of the network.
Currently, the typical annual percentage yield is 9.7% of ATOM staked annually. If users stake 1000 ATOM, they get 89.18 ATOM as rewards and 10.28% as commission on average, though it varies between validators.
Staking rewards are generated by the Cosmos Hub transaction fees and distributed to the cryptocurrency holders. It is recommended to stake with different validators simultaneously to avoid major risks if one validator misbehaves or has downtime. The delegated ATOM is forfeited (burned) and, therefore, lost in that instance.
To claim rewards at the end of the staking period, it's enough to generate a transaction with no value or costs using a wallet. There isn't a specific Cosmos wallet. Instead, various exchanges and crypto services support networks and tokens across the Cosmos ecosystem.
Web wallets include Exodus, Math wallet and Citadel One, to name a few. Ledger Live, Shapeshift, Trust wallet and many others can be used to send, receive and store ATOM.
The future of the Cosmos blockchain
The road ahead appears encouraging for the Cosmos ecosystem. Significant improvements are expected in terms of security with the development of Interchain Security. This will guarantee better protection across all the interconnected chains.
More fluidity in IBC connections will facilitate DeFi transactions and interchain NFT transfer across different public and permissioned blockchains.
Cosmos' upcoming plans are ambitious and include many more features, but it has a team of hard-working developers behind it that allows its participants to hope for a promising future.
Disclaimer : The above empty space does not represent the position of this platform. If the content of the article is not logical or has irregularities, please submit feedback and we will delete or correct it, thank you!